The New Silk Road
Contents |
[edit] What is the New Silk Road?
The Silk Road was the name given in 1877 by the German geographer Ferdinand von Richthofen to the ancient network of trade routes linking China to central and western Asia, India and the Mediterranean region.
Today, China is breathing new life into the Silk Road with the goal of forging stronger relationships with its neighbours through the development and sharing of resources.
President Xi Jinping, speaking at the World Economic Forum 2017 in Davos, referred to the ancient Silk Road, highlighting the fact that international trade is an inherent human activity that helped in the past to maintain peace and stability over long periods of time.
[edit] What is its potential?
Today, the New Silk Road, or what is known as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), has the potential to prompt a profound shift in the global order towards a new multilateralism. In a narrow sense, the BRI is primarily a strategic infrastructure initiative of historic proportions. The planning and delivery of scalable infrastructure for power generation, transportation, water supply, and telecommunications will bring much-needed economic and societal connectivity to the 65 countries along this new network.
Through the BRI, China is proposing to share its immense financial and industrial resources and capabilities, as well as its experience of four decades of reform and opening-up, while securing its own long-term development.
The BRI makes a unique contribution to international cooperation and economic development: it is based on the stakeholder approach, it seeks to leverage market forces in best ways, it prepares best for the age of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, it is built on the open-platform concept and, most importantly, it is the positive narrative the world needs.
The BRI has five major goals: policy coordination; facilities’ connectivity; unimpeded trade; financial integration; and people-to-people exchange.
Beyond the initial commitment by the Chinese government of about $1 trillion in infrastructure development, which conservative estimates believe to be viable, the BRI will require roughly an aggregate of $6 trillion for the next 15 years to finance infrastructure projects fuelling the Belt and Road economies.
During that period, the Chinese plan to cumulatively invest $4 trillion in total – about 20 times the size of the post-Second World War Marshall Plan investment of $17 billion, which has a value of about $190 billion today. Several multilateral development banks have also committed to support the BRI to accomplish those ambitious goals and finance BRI-related projects.
[edit]
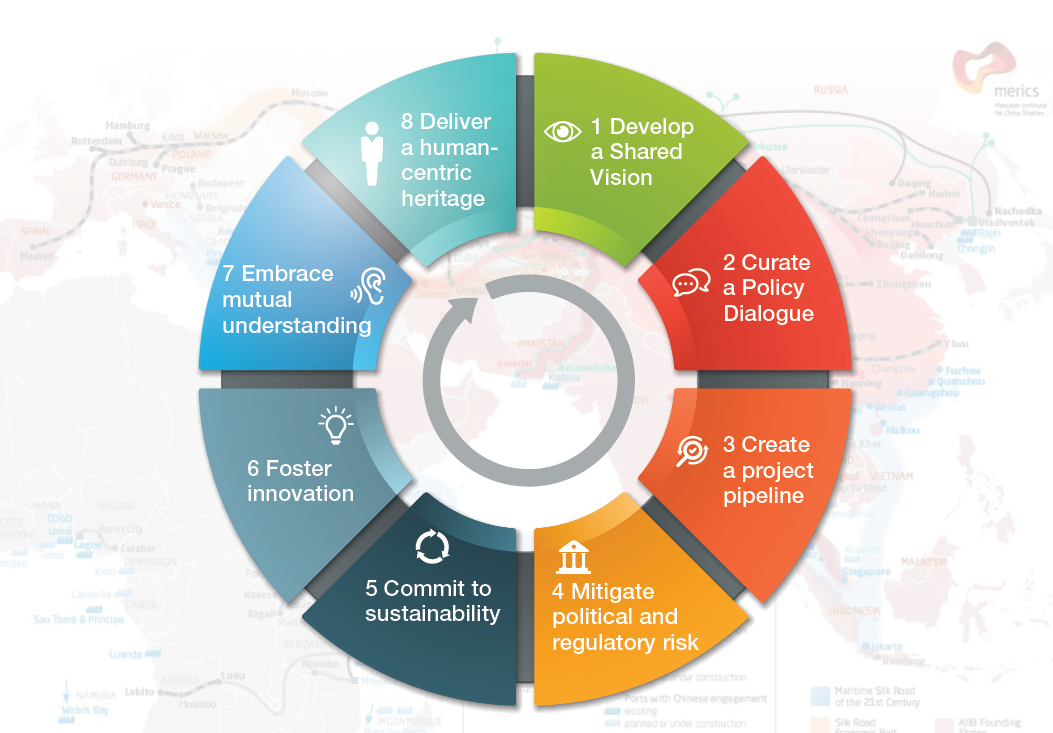
To avoid being locked into unsustainable patterns of development, which has been the common pitfall of large-scale strategic infrastructure projects, we anticipate eight transformation factors that have the potential to provide high-level stewardship for the BRI and revive the spirit of shared prosperity. These insights are derived from several years of analysing the infrastructure industry and its development projects.
To avoid being locked into unsustainable patterns of development, which has been the common pitfall of large-scale strategic infrastructure projects, we anticipate eight transformation factors that have the potential to provide high-level stewardship for the BRI and revive the spirit of shared prosperity. These insights are derived from several years of analysing the infrastructure industry and its development projects.
[edit]
Achieving transnational and international support for a shared vision for strategic infrastructure development that promotes wellbeing and a national sense of purpose to the communities beyond national borders.
[edit] Multilateralism
Curating an open and multilateral policy dialogue that addresses public-private-civic cooperation, early-stage project financing, standardized procurement and transparency, to level the playing field and build trusted relationships.
[edit] Project-preparation facility
Creating an infrastructure project-preparation facility to ensure a pipeline of bankable projects and a transnational centre of excellence to deliver the largest portfolio of projects ever.
[edit] Risk mitigation
Proactively mitigating political and regulatory risk to boost stakeholder engagement and confidence in the plan by investors, off-takers and operators.
[edit] Sustainable development
Committing to sustainability, inclusion and affordability principles to generate value for future generations beyond Agenda 2030.
[edit] Innovation
Enhancing technological and business model innovation for sustained value creation, ensuring readiness for the future.
[edit] People-to-people exchange
Governing domestic and cross-border migration and promoting mutual learning and understanding, to enable and deepen people-to-people exchange and transnational cultural cooperation, ensuring transcendent growth and universal purpose.
[edit] Human-centric and future-ready
Delivering the new humane infrastructure heritage beyond the current infrastructure usage for the next millennium.
Read more on what it takes to implement the eight steps towards shared prosperity and a sustainable future here.
Written by
- Michael Buehler, Head of Infrastructure & Urban Development, World Economic Forum
- Thorsten Jelinek, Director, Taihe Institute
- Sergio Gusmao Suchodolski, Director General, Strategy and Partnerships, New Development Bank (NDB)
- Pedro Rodrigues De Almeida, Member B20 Task Force on Financing Growth & Infrastructure, B20 Germany
- Olivier M. Schwab, Head of Business Engagement - Member of the Managing Board, World Economic Forum
[The views, opinions and positions expressed by author Sergio Suchodolski are his alone, and do not necessarily reflect the views, opinions or positions of the New Development Bank.]
--Future of Construction 13:39, 24 Oct 2017 (BST)
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- A better investment framework for Africa.
- China - clean, green buildings of the future.
- How Latin America and the Caribbean can unlock their digital potential.
- India needs to build more infrastructure fast. Here’s how.
- Scoping project approach in the developing world.
- State of the construction industry in Uganda.
- These giant infrastructure projects are set to reshape Africa.
- Top architectural wonders of Dubai.
- Why the West has to join the Belt and Road Initiative.
Featured articles and news
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help the homebuilding sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.